No one likes to take the time to make passwords online. When you’re setting up your CBSSports account to fill in your March Madness brackets, you just want to get to work. No one’s going to hack you, so you just use the same password there as you do for your Bank of America account and GMail. Who cares, right? You’ve got nothing to hide.
And then you get “hacked” and it’s no fun.
Being a “techy” person, I get lots of questions about how to avoid being “hacked” (it’s fascinating to me how that word has changed its usage as geek and tech culture has become mainstream).
My response is normally:
1) Never use the same password twice. Ever. Use a service such as LastPass if you’re into that (I am).
2) For each of the online services you use, make unique and long passwords that include random characters and even nonsense strings that only you know (I know, I know… this isn’t completely foolproof but it helps prevent the script kiddie hacks). Try to avoid common terms such as “password,” “changeme,” or “123456.”
3) Never use the same password twice. Ever.
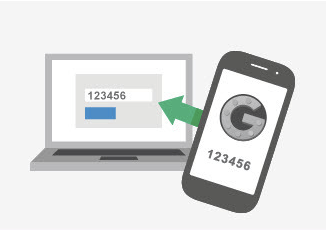
4) If you can, enable 2 Factor Authentication.
5) Never use the same password twice. Ever.
Step 1 is usually when the person loses interest in my advice. But you should really enable Two Factor Authentication (2FA) as soon as possible if you’re at all concerned about your online accounts or just want to have a good lock on your doors to keep honest people honest.
TwoFactorAuthor.org has a nice list of major services that we all use, with links to relevant instructions, such as Google Accounts, Dropbox, Twitter, Facebook, even Steam or Etsy etc.
There’s no reason for you not to do this today.
Two-factor authentication! In this age of endless massive hacks we seem to be in the middle of, it’s one of the easiest ways you can dramatically boost security on your online accounts.
But which sites actually support it? It can be a pain to keep track. Fortunately, a new, community-driven list keeps a running list of all the big sites that have some form of 2FA enabled (and encourages you to nag at those that don’t).
via Here Are All The Sites You Should Enable Two Factor Authentication On (And The Ones You Should Yell At) | TechCrunch.


